Cool Tips About How To Treat Ranula

How is a ranula treated?
How to treat ranula. How is a ranula treated? The following are the most common treatment approaches. Plunging ranula is a condition that presents as painful neck swelling, often in younger patients.
The simplest treatment is marsupialization. How is a ranula diagnosed? Causes, symptoms, and treatments | colgate® more articles overview.
It is filled with saliva (spit) that has leaked out of a damaged salivary gland. Salivary gland infection?
A ct scan is used in rare cases when a ranula has grown into your neck. Murakami improving children's lives through innovative imaging overview causes diagnosis signs & symptoms treatment seeking help what is a ranula? But you should see a doctor for an enlarged ranula since there’s the risk of the.
1 (0%) combined transoral and cervical approach: Mucocele, which is of minor salivary gland origin, arises when there is a disruption of the flow of its secretions. Smaller ranulas that need treatment can be aspirated.
Aim the aim of this paper was to systematically review the available literature on the management of paediatric oral ranula. The usual treatment for a ranula is surgical removal of the blocked salivary gland. How can you treat ranulas?
23% of head and neck surgeons prefer to treat a plunging ranula with excision of the ranula along with the removal of the sublingual and submandibular gland. Around the posterior edge of the mylohyoid muscle, or. [1] ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging may be useful to image the lesion.
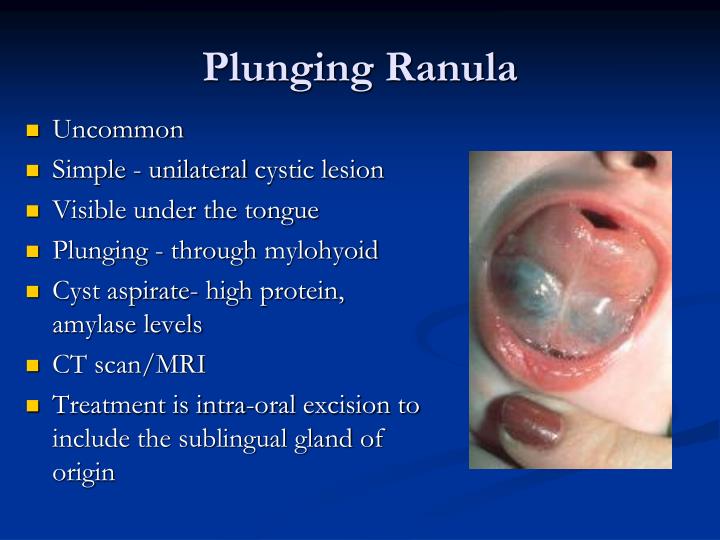
Ranula is mucous extravasation cyst that occurs in the floor of the mouth. A ranula forms due to a blocked or damaged major salivary gland. Computed tomography (ct) scan:
Submandibular and sublingual gland excision plus ranula excision: When a ranula starts interfering with your regular activities, your doctor may recommend making an incision to drain its fluid. This procedure can be performed in the clinic with a cooperative patient or under general anesthesia.
When a ranula “plunges” through weaknesses in the floor of the mouth to enter the neck, it can present as a painful neck swelling. Extravasation mucoceles and retention mucoceles. Possible causes and treatment options when is a cold sore no longer contagious?